News Story
AHRI Grant Supports Study of Refrigerant Flammability

The Air-Conditioning, Heating, and Refrigeration Institute (AHRI) has awarded the University of Maryland’s Department of Fire Protection Engineering (FPE) a $150,000 grant to support research on refrigerant flammability. The project, titled Investigation of Energy Produced by Potential Ignition Sources in Residential Application, will be led by Associate Professor Peter Sunderland and Research Associate Dr. Vivien Lecoustre. The project started in April 2015 and will end October 2016.
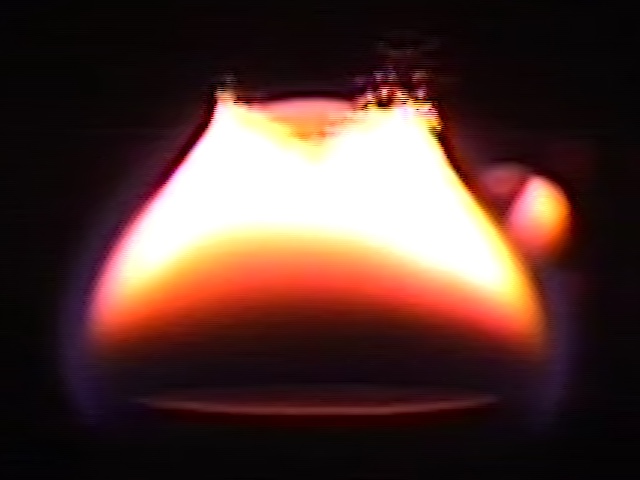
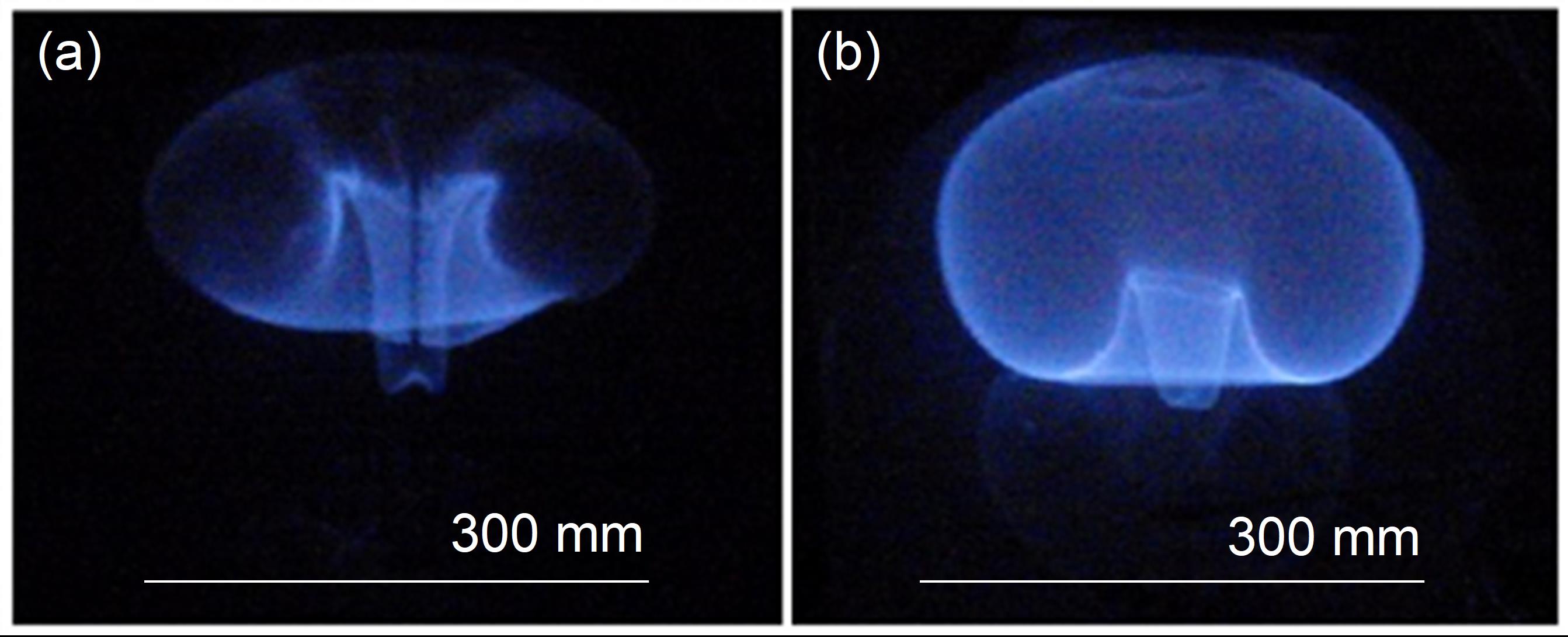
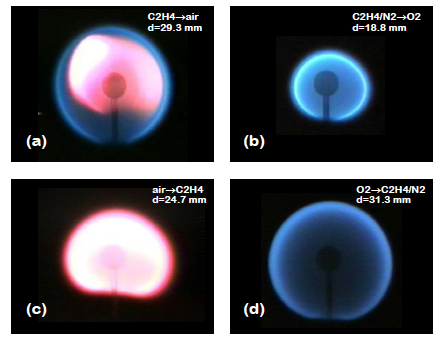
An international drive toward sustainability of refrigeration systems will require the adoption of low global warming potential (GWP) refrigerants. Most of these are mildly flammable, which has motivated extensive research. Owing to concerns about fire safety, the first to be adopted will be classified A2L, or A1 but very close to the border with A2L. The A2L designation requires a lower flammability limit (LFL) above 3.5%, a heat of combustion below 19 kJ/g, and a laminar flame speed below 10 cm/s.
Low-GWP refrigerants are generally well-characterized in terms of their LFLs, heats of combustion, and flame speeds. However, they are poorly understood in terms of their susceptibility to ignition from sources commonly encountered in household and industrial settings, including open flames, electric arcs, and hot surfaces. This adds large uncertainties to any risk assessment of A2L refrigerants. This important gap in understanding is the focus of this research.
Sunderland and Lecoustre’s project is divided into three main tasks: perform a detailed literature survey; develop an ignition test plan; and perform the ignition tests.
Published November 2, 2015