Overview
ASTM E162 provides a convenient relative measure of the flame spread and heat evolution performance of building materials. The test has not enjoyed the widespread adoption of ASTM E84, perhaps due to misconceptions concerning its ability to connect to E84 flammability performance measurements. Nevertheless, when viewed within its own frame of reference, this test method provides a valid flammability assessment. ASTM E162 is currently applied to materials for rapid rail transit and light rail transit vehicles and military applications among others.
Setup
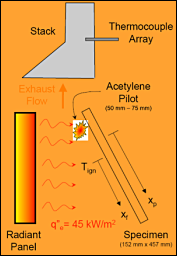
Vertical radiant panel test exposure configuration.
After ignition, the downward opposed flow flame spread rate and exhaust stack temperature rise are measured simultaneously to determine a flame spread factor and heat evolution factor which are combined into a single radiant panel index for assessing material flammability.
Analysis
|
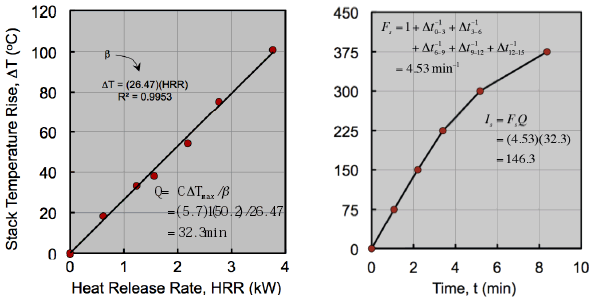
Test calibration plot for determining relationship between heat evolution & stack temperature rise, β. Calibration performed by measuring temperature rise from flames produced w/ a methane calibration burner over a range of fuel flow rates. A heat evolution factor, Q, is determined from max temp rise during specimen testing and β. |
Flame front propagation plot for 4.8 mm hardboard. Elapsed times between successive 75 mm (3”) intervals are used to determine a flame spread factor, Fs. Fs is combined with Q yielding an overall flammability parameter, the radiant panel index, Is. |
Top